Simple meshing
Module: tutorials.11_academy.01_meshing.run
Section author: Gernot Plank <gernot.plank@medunigraz.at>
Overview
The objectives in this section are to learn the use of mesher for:
- Generating of simple slab/wedge-like meshes
- Controling the assignment of fiber and sheet arrangements
- Defining regions by tagging elements
Details on mesher functions are given here.
Task 01: Build a simple slab mesh
Use mesher to be build a discrete slab model according to the following specifications:
length (x-direction) : 4.0 cm width (y-direction) : 4.0 cm depth (z-direction) : 0.025 cm resolution : 250 :math:`\mu m`isotropic
Label the mesh using the basename thinwedge.
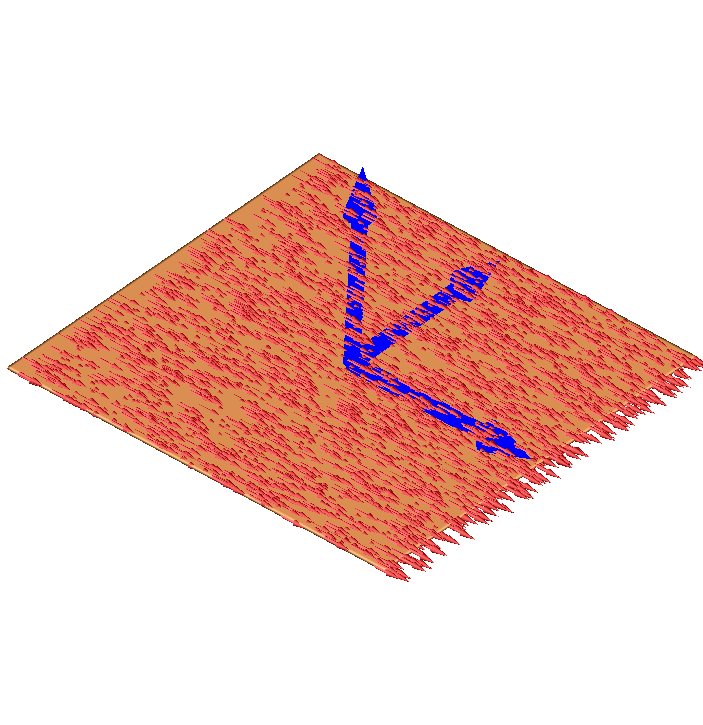
Use meshalyzer and meshtool to verify that the mesh follows the prescribed specifiations
- Compute the size of the bounding box using meshtool
- Visualize the fiber orientations with meshalyzer
Task 02: Build a simple slab mesh immersed in a bath
Use the same specs as in Task 01, but immerse the slab in a bath. Use the following bath dimensions:
bath (x-direction) : 0.5 cm bath (y-direction) : 0.5 cm bath (z-direction) : 0.05 cm resolutio : 250 :math:`\mu m`isotropic
Label the mesh using the basename thinwedge-bath.
Use meshalyzer and meshtool to verify that the mesh follows the prescribed specifiations
- Compute the size of the bounding box using meshtool
- Visualize the mesh using meshalyzer, assign different colors to bath and tisue
# .. meshtool query bbox -msh=./thinwedge
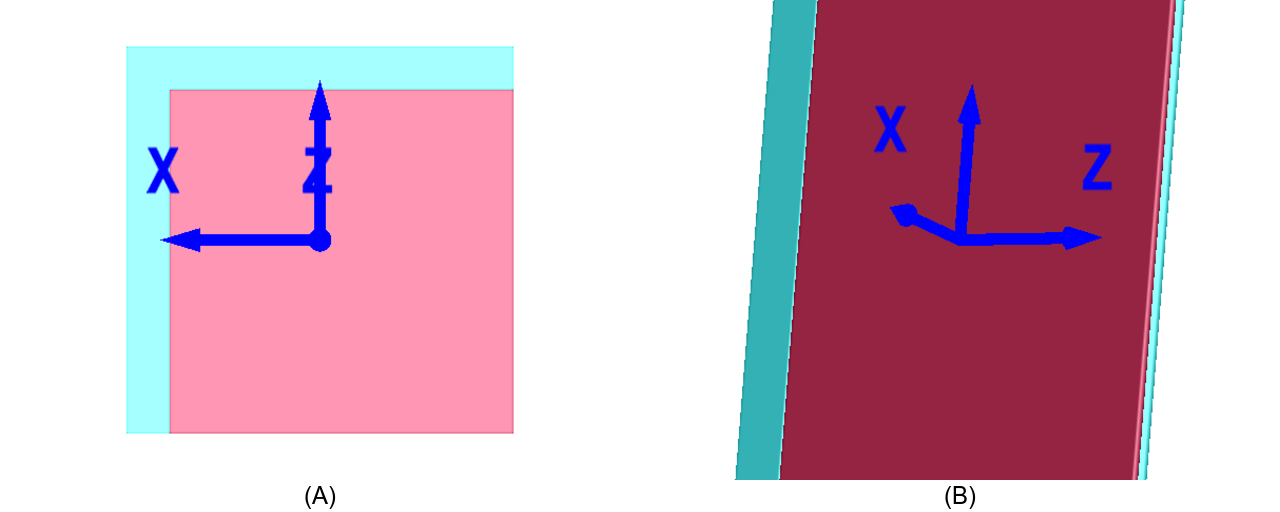
Fig. 168 Verification of added bath which is only added to
 .
Shown is meshalyzer with colored tags (Tag 0: bath in blue; Tag 1: tissue in red).
Details on region tags are found in the tagging tutorial
and the region section of the manual.
.
Shown is meshalyzer with colored tags (Tag 0: bath in blue; Tag 1: tissue in red).
Details on region tags are found in the tagging tutorial
and the region section of the manual.
Task 03: Build a simple slab mesh with a central circular region
- Use the same specs as in Task 01, but add a
circular region of radius
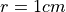 to the center of the tissue.
to the center of the tissue.
Task 04: Build a simple wedge mesh with rotating fibers
Use the same specs as in Task 01, but increase the transmural depth
 to twice the spatial resolution of the mesh such that two layers of elements are built.
to twice the spatial resolution of the mesh such that two layers of elements are built.Note
Tensors are assigned on a per element basis. Thus, to allow for transmural fiber rotation at least two element layers are nessecary.