Mechanical Boundary Conditions
Module: tutorials.04_EM_tissue.01_boundary_conditions.run
Section author: Christoph Augustin <christoph.augustin@medunigraz.at> andMatthias Gsell <matthias.gsell@medunigraz.at>
This tutorial demonstrates the time-dependent application of different boundary condition types, i.e., Dirichlet and Neumann boundary conditions, on a cuboidal geometry. For more details on the definition of mechanical boundary conditions in carpentry see manual section mechanical boundary conditions.
Geometry and Material Definition
A simple tetrahedral finite element mesh of a cube shown in Fig. 128 with side length 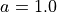 mm and resolution
mm and resolution 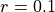 mm as default is generated. The cube is assigned a neo-Hookean material model with shear modulus
mm as default is generated. The cube is assigned a neo-Hookean material model with shear modulus 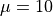 kPa and penalty parameter
kPa and penalty parameter 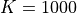 kPa.
kPa.
Boundary Condition Application
For the experiments I & II, movement of nodes located at 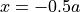 is restricted in all directions, i.e., homogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions are applied (see left and right panels in Fig. 128).
is restricted in all directions, i.e., homogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions are applied (see left and right panels in Fig. 128).
Experiment I - Dirichlet Boundary Conditions
Experiment I provides guidance on the consistent application of inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions (see left panel in Fig. 128). Nodes located at 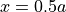 are translated under application of displacement
are translated under application of displacement ![\mathbf{u} = [u_{1},0,0]^{\mathrm{T}}](../../_images/math/89e2bab1597adfe3e8c80985999d384a85262bf8.png) utilizing the command line
utilizing the command line
./run.py --experiment dirichlet --sidelength 1.00 --resolution 0.10 --magnitude 0.10 --visualize
where the parameter experiment selects the correct boundary condition type, parameters sidelength and resolution provide an optional input for the mesh generation and magnitude defines the displacement 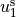 in mm. The application of inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected displacement is provided calculated as
in mm. The application of inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected displacement is provided calculated as ![\mathbf{u} = \phi \mathbf{u}^{\mathrm{s}} = \phi [u_{1}^{\mathrm{s}},u_{2}^{\mathrm{s}},u_{3}^{\mathrm{s}}]^{\mathrm{T}}](../../_images/math/5632f5a7fa421a64b242cf46c51b86b18aaa166a.png) , where
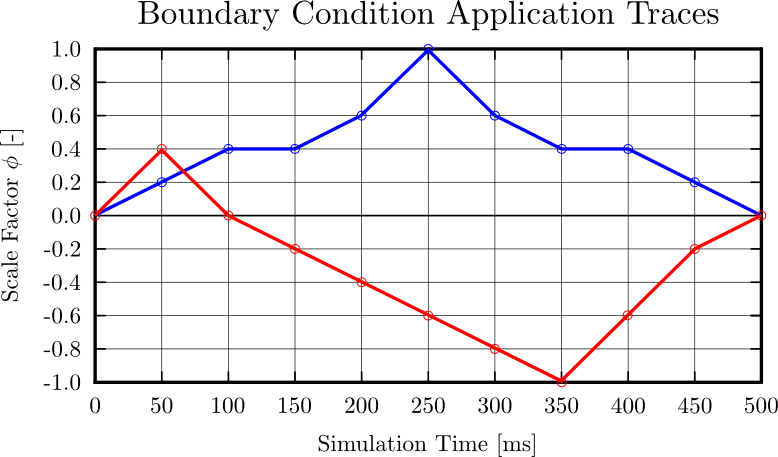
, where 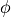 represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
Note
Node selection for application of Dirichlet boundary conditions is currently based on internal functions, but can alternatively be performed utilizing a vertex file (.vtx).
Experiment II - Neumann Boundary Conditions
Experiment II provides guidance on the consistent application of Neumann boundary conditions (see right panel in Fig. 128). Nodes located at 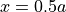 are translated under application of pressure
are translated under application of pressure 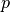 on the corresponding surface triangles utilizing the command line
on the corresponding surface triangles utilizing the command line
./run.py --experiment neumann --sidelength 1.00 --resolution 0.10 --magnitude 5.00 --visualize
where the parameter experiment selects the correct boundary condition type, parameters sidelength and resolution provide an optional input for the mesh generation and magnitude defines the applied pressure 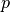 in kPa. Again, the application of Neumann boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected pressure is provided calculated as
in kPa. Again, the application of Neumann boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected pressure is provided calculated as 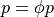 , where
, where 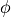 represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
Note
Element selection for application of Neumann boundary conditions is currently based on internal fuctions, but can alternatively be performed utilizing a surface element file (.neubc).
Experimental Results
Upon application of the command lines introduced above, results provided in Fig. 130 will be obtained. While in Experiment I inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions are consistently stretching the cube, Neumann boundary conditions in Experiment II administer both, compression and tension on the cube (compare boundary condition application traces in Fig. 129).
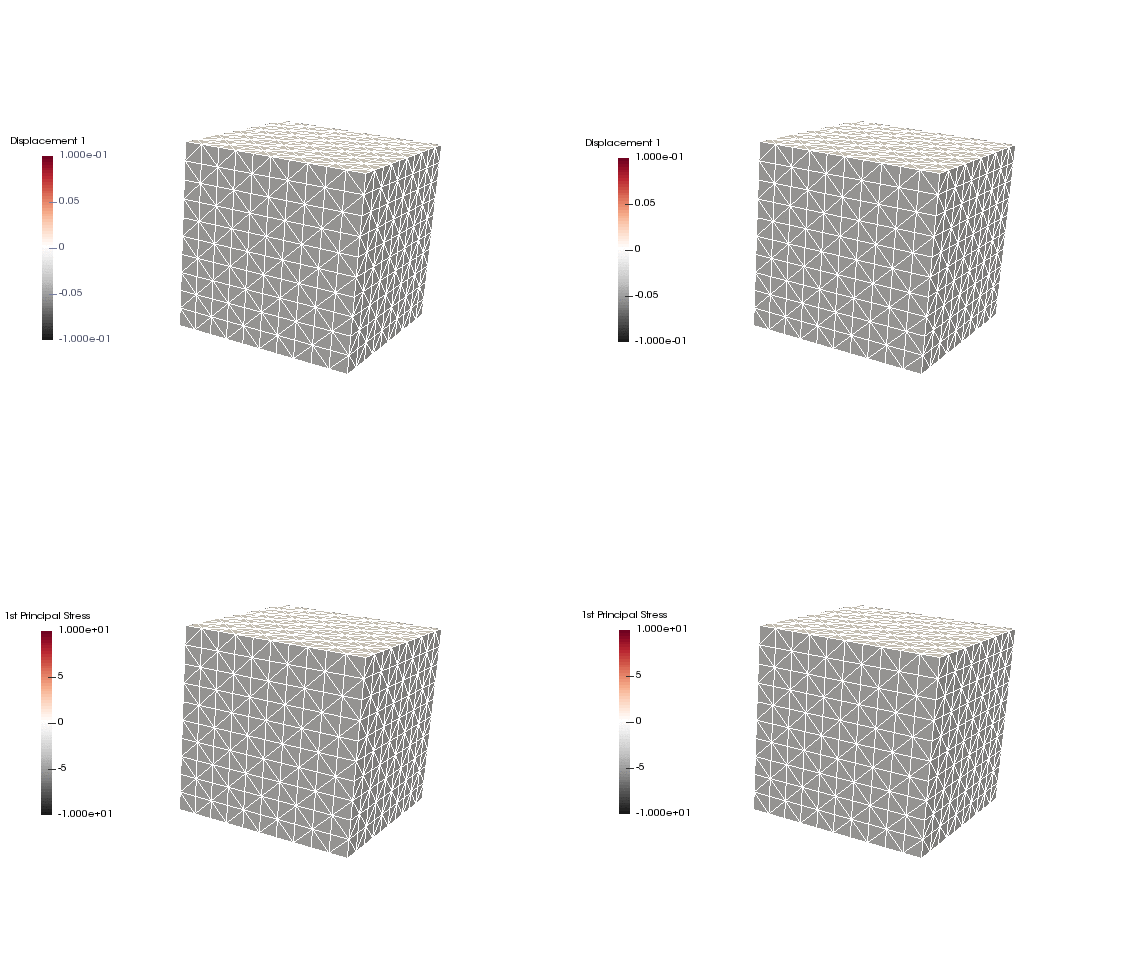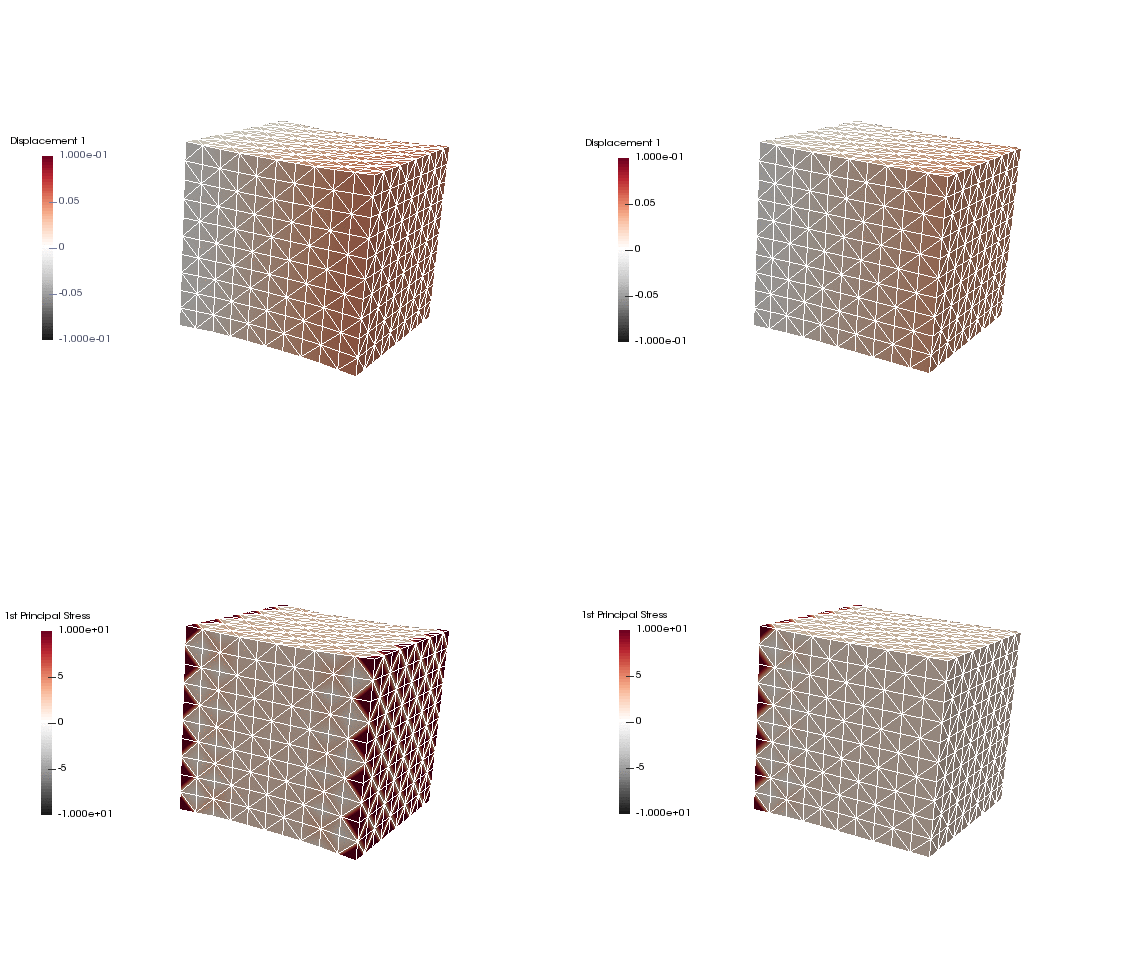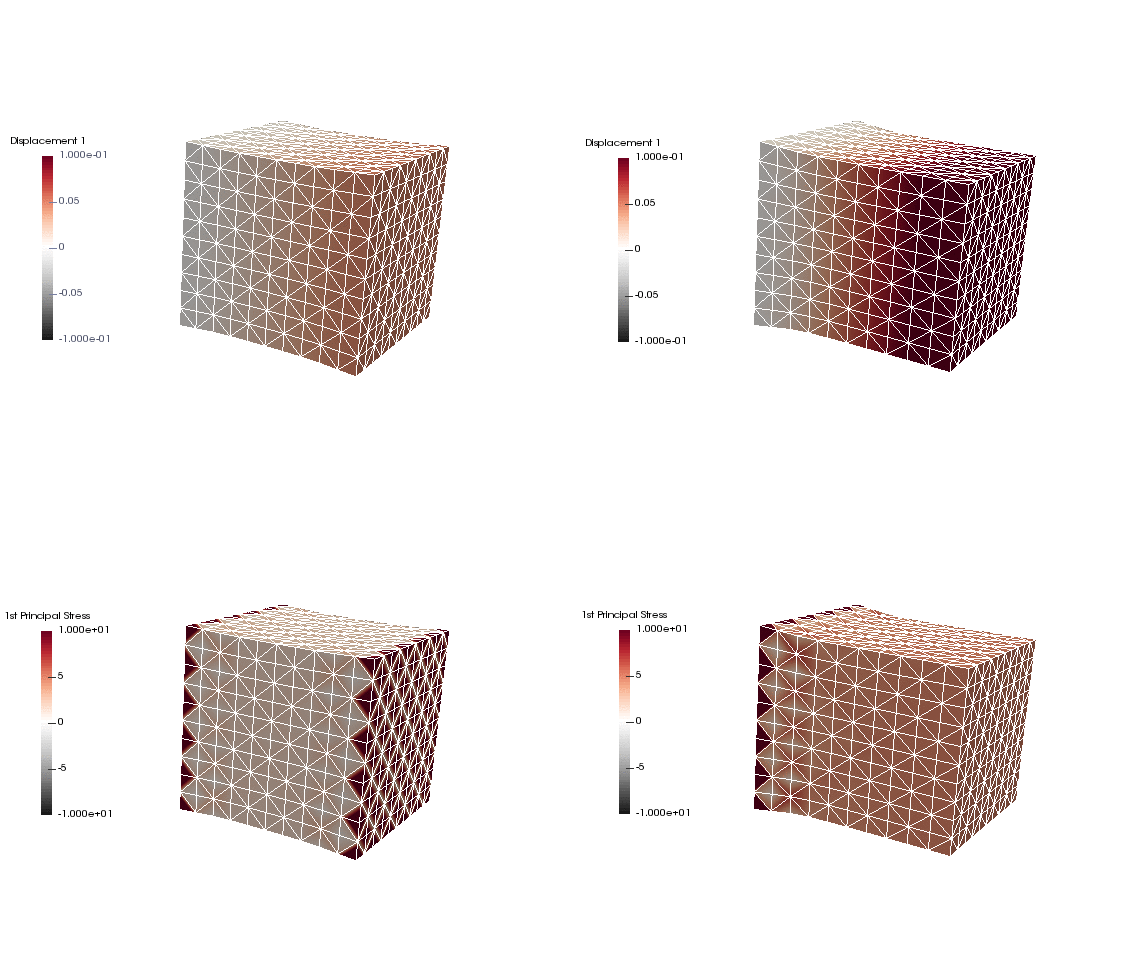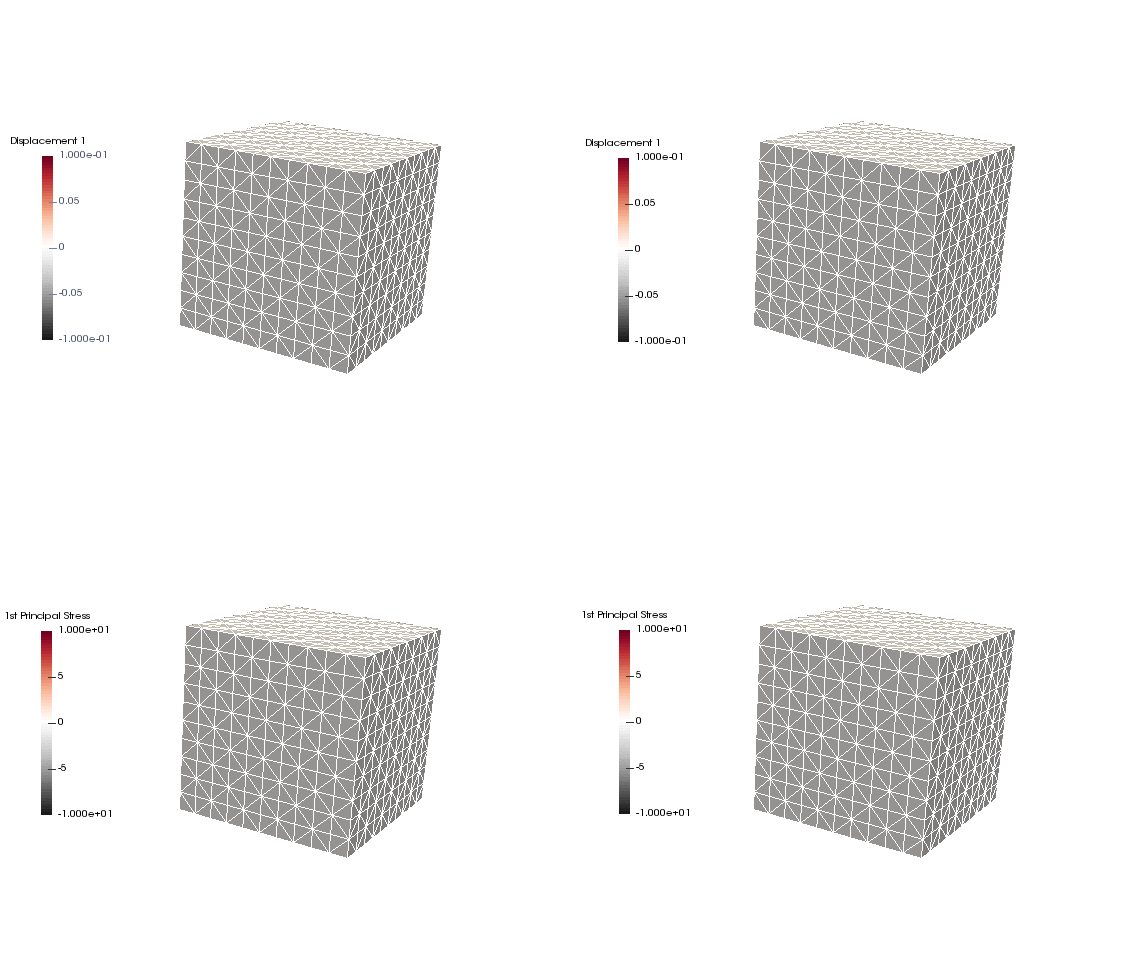
Fig. 130 Results obtained upon application of command lines introduced in Experiment I using Dirichlet boundary conditions (left panel) and Experiment II using Neumann boundary conditions (right panel) with the color-code representing displacement in 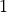 -direction (top row) and
-direction (top row) and  principal stress (bottom row).
principal stress (bottom row).
For the experiments III & IV, the plane at 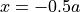 is attached to a spring acting in all directions, i.e., homogeneous Robin boundary conditions are applied.
is attached to a spring acting in all directions, i.e., homogeneous Robin boundary conditions are applied.
Experiment III - Dirichlet Boundary Conditions
Experiment III provides guidance on the consistent application of inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions (see left panel in Fig. 128). Nodes located at 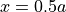 are translated under application of displacement
are translated under application of displacement ![\mathbf{u} = [u_{1},0,0]^{\mathrm{T}}](../../_images/math/89e2bab1597adfe3e8c80985999d384a85262bf8.png) utilizing the command line
utilizing the command line
./run.py --experiment dirichlet --fixation weak --sidelength 1.00 --resolution 0.10 --magnitude 0.10 --visualize
where the parameter experiment selects the correct boundary condition type, parameters sidelength and resolution provide an optional input for the mesh generation and magnitude defines the displacement 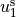 in mm. The application of inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected displacement is provided calculated as
in mm. The application of inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected displacement is provided calculated as ![\mathbf{u} = \phi \mathbf{u}^{\mathrm{s}} = \phi [u_{1}^{\mathrm{s}},u_{2}^{\mathrm{s}},u_{3}^{\mathrm{s}}]^{\mathrm{T}}](../../_images/math/5632f5a7fa421a64b242cf46c51b86b18aaa166a.png) , where
, where 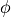 represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
Note
Node selection for application of Dirichlet boundary conditions is currently based on internal functions, but can alternatively be performed utilizing a vertex file (.vtx).
Experiment IV - Neumann Boundary Conditions
Experiment IV provides guidance on the consistent application of Neumann boundary conditions (see right panel in Fig. 128). Nodes located at 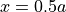 are translated under application of pressure
are translated under application of pressure 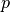 on the corresponding surface triangles utilizing the command line
on the corresponding surface triangles utilizing the command line
./run.py --experiment neumann --fixation weak --sidelength 1.00 --resolution 0.10 --magnitude 5.00 --visualize
where the parameter experiment selects the correct boundary condition type, parameters sidelength and resolution provide an optional input for the mesh generation and magnitude defines the applied pressure 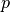 in kPa. Again, the application of Neumann boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected pressure is provided calculated as
in kPa. Again, the application of Neumann boundary conditions is time-dependent and necessitates existence of a specific trace file (.trc), in which the time course for the selected pressure is provided calculated as 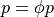 , where
, where 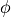 represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
represents the scale factor (see Fig. 129).
Note
Element selection for application of Neumann boundary conditions is currently based on internal fuctions, but can alternatively be performed utilizing a surface element file (.neubc).
Experimental Results
Upon application of the command lines introduced above, results provided in Fig. 131 will be obtained. While in Experiment III inhomogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions are consistently stretching the cube, Neumann boundary conditions in Experiment IV administer both, compression and tension on the cube (compare boundary condition application traces in Fig. 129).
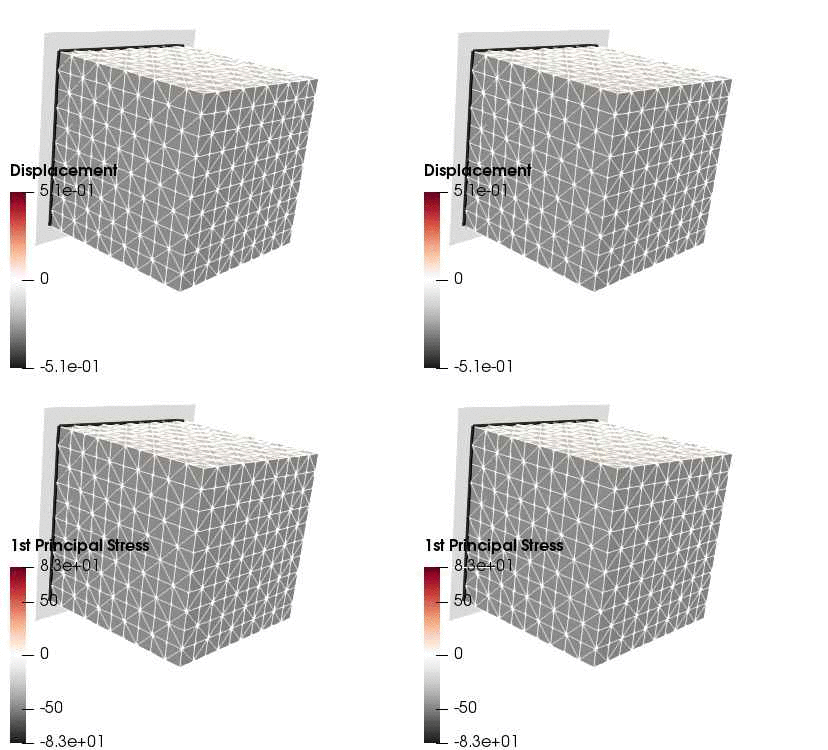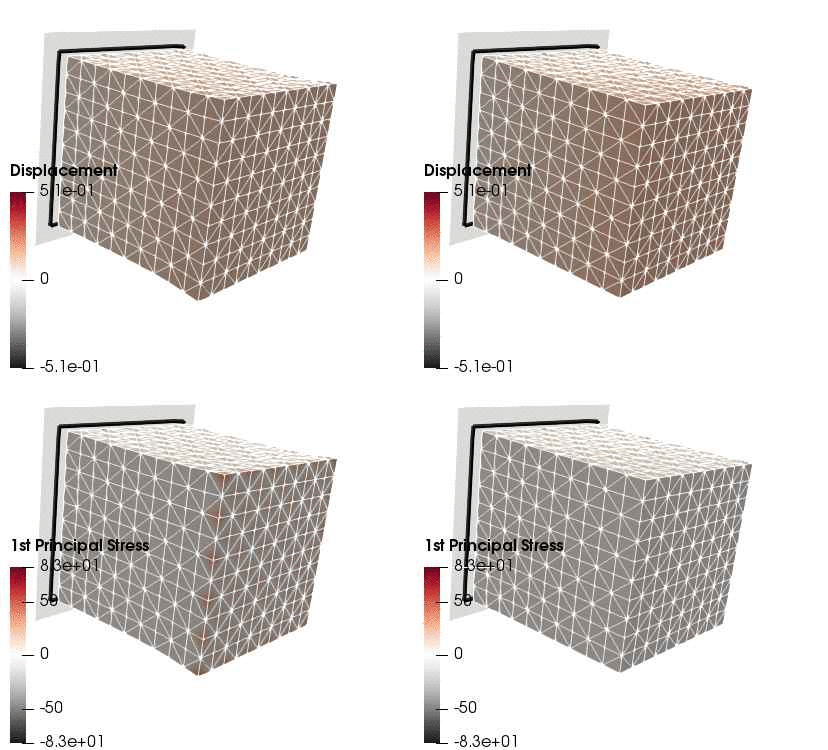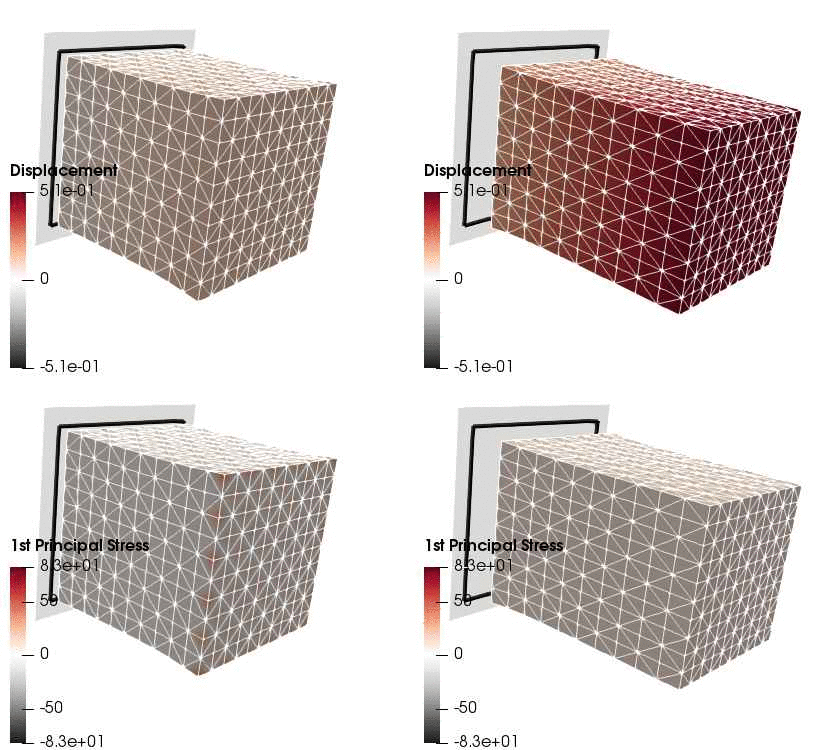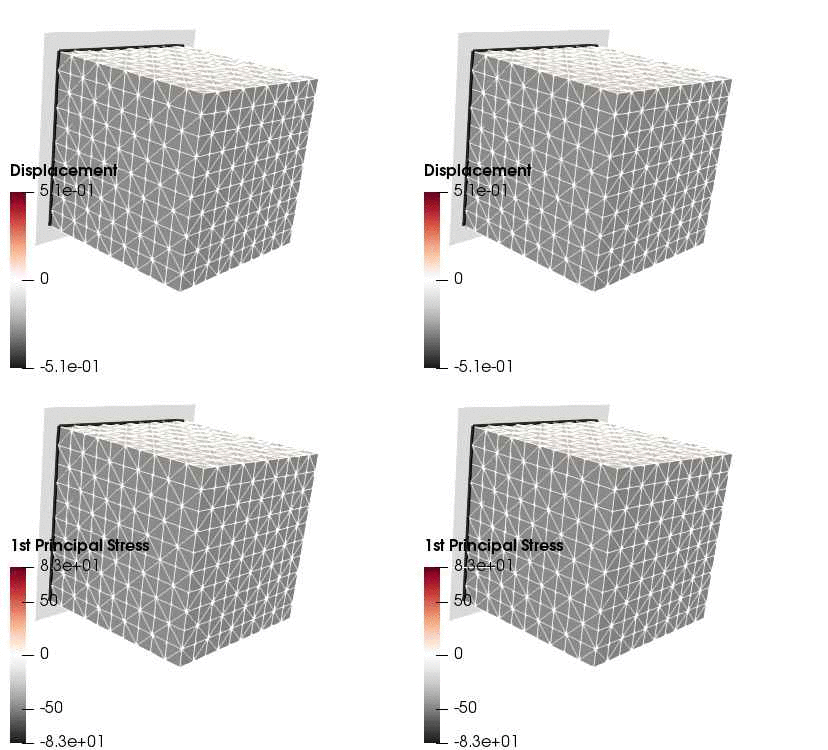
Fig. 131 Results obtained upon application of command lines introduced in Experiment III using Dirichlet boundary conditions (left panel) and Experiment IV using Neumann boundary conditions (right panel) with the color-code representing displacement in 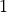 -direction (top row) and
-direction (top row) and  principal stress (bottom row).
principal stress (bottom row).